What is the Role of Business Intelligence in Finance?
Tarsem Singh | April 4, 2025 , 15 min read
Table Of Content
Imagine a scenario where a seasoned financial professional is surrounded by spreadsheets, each containing vital information for critical decisions. Picture the pressure they face as they sift through each piece of data, trying to figure out something useful. Taking the wrong turn will have consequences; there is no room for error in the financial sector. Every decision has to be precise and backed by data. However, human errors are inevitable, even for seasoned professionals.
The finance professional faces a tough situation: matching data with long-term goals. While making timely decisions is crucial in finance, the abundance of complex information makes it difficult to do so quickly. This situation is common in finance—managing lots of reports, each important, but struggling to see the whole picture.
Fortunately, there is a solution: Business Intelligence (BI). BI not only consolidates and interprets data but also can turn them into useful insights to help make precise decisions, eliminating guesswork and enabling finance professionals to make better decisions by making the path clearer.
In this blog post, we will look at BI’s role in finance and how it gives finance professionals the confidence and precision they need in their line of work.
Key Takeaways
- BI empowers finance professionals to transform data into actionable insights, enabling informed decisions, strategic planning, and proactive risk management.
- Financial BI systems automate data collection, storage, analysis, and reporting, offering real-time insights through dashboards and simplified reports for decision-makers.
- BI enhances forecasting, risk management, compliance, and operational efficiency, providing real-time metrics for better strategic decisions.
- BI is used for financial performance monitoring, budgeting, forecasting, risk management, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
- Companies like American Express use BI for fraud detection, while CitiBank leverages it for personalized customer services and operational efficiency.
What is Business Intelligence?
- What is Business Intelligence?
- How Do BI Systems Work?
- Benefits of BI in Finance
- How is BI Used in Finance? Practical Use Cases of Financial BI
- Examples of BI Applications in Finance
- Common Challenges in Implementing Financial Business Intelligence
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Further Reading: Business Intelligence Applications Across Sectors
First, let’s define what business intelligence is. Business Intelligence (BI) is a technology used for analyzing business data. It helps calculate important performance metrics and shows how they change over time, which helps improve decision-making based on data. To work effectively, a BI system requires good-quality data. Financial records collected during business operations are an important source of such data. By using BI tools for finance, businesses can gain insights into their operations and use this information to update financial metrics, improve supply chains, and make better decisions across various areas like marketing, mergers, and acquisitions.
To summarise,
- Business Intelligence (BI) is a technology that helps businesses analyze their data.
- It calculates key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure how well the business is doing.
- BI tools visualize this data, making it easier to understand and use for decision-making.
- To work well, BI needs high-quality data from sources like financial records.
- BI can help businesses improve their operations, marketing, and other areas by making better-informed decisions based on data.
Before we proceed, Business Intelligence (BI) and Business Analytics (BA) are often mistaken for one another, but they are distinct concepts. BI focuses on delivering accurate information to the appropriate individuals in a timely and effective manner. For instance, a CFO might use BI to review last month’s financial data and make plans for the coming month based on that information. On the other hand, BA is more analytical in nature, involving the use of data to forecast future trends. With BA, a financial director could analyze how specific processes have impacted income and develop models to predict future changes.
What Does Business Intelligence Mean in Finance?
Financial Business Intelligence (BI) transforms raw data into insightful stories that help you make smarter decisions. By gathering information from sources like accounting software and market records, BI efficiently streamlines how you track revenue, costs, and profit margins, while uncovering hidden risks.
This user-friendly approach gives finance teams a real-time snapshot of their finances, leading to more accurate forecasts, better budgeting, and proactive strategies for lasting growth and enhanced resilience.
How Do BI Systems Work?
The BI system operates in the following manner:
- Data Collection: It automatically retrieves data from various company systems like CRM and ERP.
- Data Storage: The collected data is often extensive and must be stored for easy retrieval.
- Analytics: BI tools extract data from the storage to conduct different analyses, displaying KPIs and allowing real-time monitoring of changes.
- Reporting: The system ensures that the data and analyses are effectively communicated to decision-makers in a format that is easy for those with limited context to understand and use.
Benefits of BI in Finance
So, the benefits. BI plays an important role in finance by offering numerous advantages beyond basic reporting. It is an analytical tool that gives a comprehensive overview of financial information. It converts raw data into useful information, aiding in forecasting, managing risks, and developing strategic plans. Finance professionals who use BI benefit from improved operational efficiency, fewer mistakes, and better compliance, leading to a proactive financial environment.
In a competitive financial environment, BI gives stakeholders immediate access to vital metrics, allowing them to make quick, well-informed decisions. The capability to identify patterns and irregularities in financial data gives businesses a strategic edge, enabling them to adapt rapidly to market changes and take advantage of new opportunities.
How is BI Used in Finance? Practical Use Cases of Financial BI
Business intelligence (BI) is widely used in finance for various purposes, reflecting the diverse nature of the financial sector. It helps improve budgeting, forecasting, and financial reporting processes, driving operational efficiency. One notable application is fraud detection, where BI algorithms analyze transactions to spot anomalies and reduce financial risks.
Here are some more examples of how BI is used in finance:
1. Financial Performance Monitoring
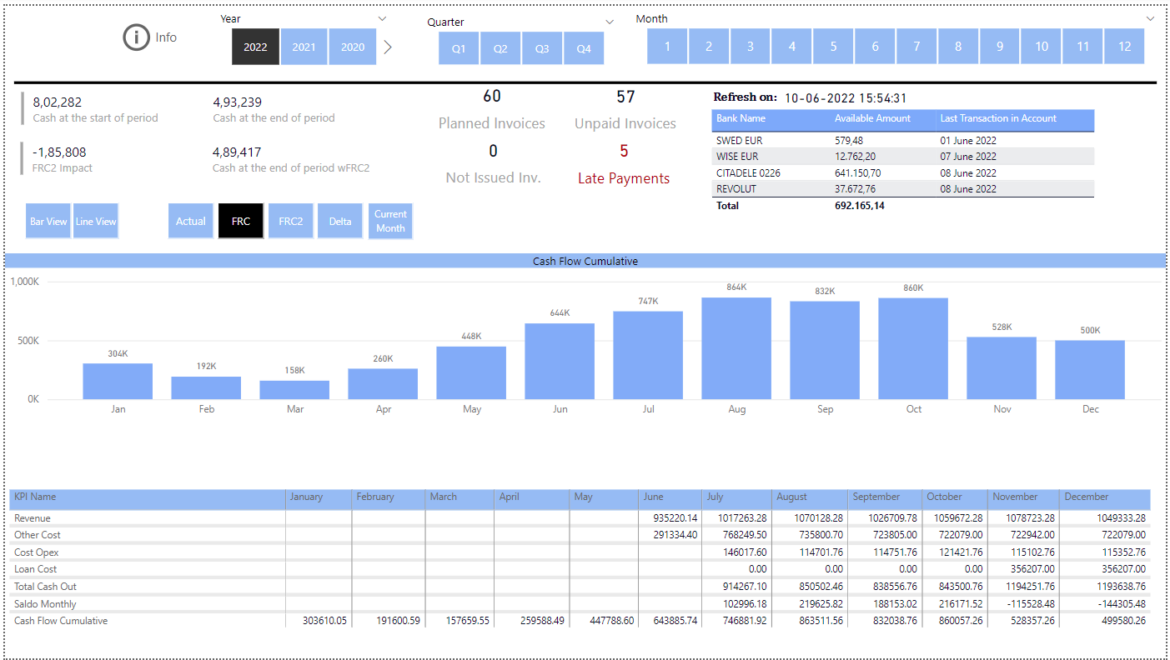
Monitoring financial performance involves using Business Intelligence methods and tools to monitor and understand financial metrics like income, costs, and profitability. This is an important part of using BI in finance because it can help finance teams find ways to save money and make new sources of income. For example, BI can be used to:
- Create Dashboards: These are interactive screens displaying real-time financial information such as sales, costs, and profitability. Finance teams, management, and investors can use these dashboards to monitor financial performance.
- Generate Financial Reports: BI can be used to produce detailed reports on financial performance. These reports help analyze trends and patterns in financial data and track changes in performance over time.
- Conduct Budget vs Actual Analysis: BI can compare planned budgets with actual financial performance. This analysis helps finance teams identify discrepancies and take corrective actions.
2. Budgeting and Forecasting
Budgeting and forecasting involve using Business Intelligence (BI) methods and tools to predict how a company will perform financially in the future. This is a crucial part of using BI in finance because it helps finance teams create accurate budgets and forecasts, which are essential for making strategic plans and decisions. For instance, BI can be used in the following ways for budgeting and forecasting:
- Analyzing historical data: BI enables the analysis of past financial data such as sales, expenses, and profits. This analysis can be used to predict future financial performance and identify trends and patterns in past financial data.
- Developing forecasting models: BI can be used to create models that forecast future financial performance based on historical data and statistical methods. These models can factor in various variables such as market trends, economic conditions, and company-specific information.
- Comparing budgets and forecasts: BI allows finance teams to compare actual financial performance with planned and predicted data. This comparison helps them identify any discrepancies and take corrective actions as needed.
3. Risk Management
Leaders need to respond promptly to threats. Risk management involves spotting, evaluating, and lessening potential risks that could impact a company’s financial performance. Business Intelligence (BI) can aid risk management by giving organizations the tools to find and judge risks and check if their risk management plans are working. For example:
- Identifying risks: BI can look at financial data to find possible risks like credit, market, and operational risks. This helps organizations find and handle risks early on.
- Assessing risks: BI can determine how likely and serious identified risks are. This helps organizations decide which risks to handle first.
- Reporting risks: BI can make reports that detail how risks are doing and how well risk management plans are working. These reports can tell important people like managers and investors about how risk management is going.
4. Compliance and Regulatory Reporting
In finance, compliance means ensuring that a company’s financial practices and reports meet legal and industry standards. Business Intelligence (BI) can help with compliance by giving organizations the tools they need to keep track of their financial performance in the following ways:
- Regulatory Reporting: BI can be used to generate reports that regulatory agencies like the SEC, FDA, and IRS require. These reports contain detailed financial data and help ensure the organization follows accounting rules.
- Audit Trails: BI can create audit trails that track changes made to financial data. These trails are helpful during audits because they provide a record of all financial activities.
- Compliance Monitoring: BI can be used to create automated systems that look for potential compliance issues. This helps organizations identify and address problems before they become serious violations.
- Compliance Reporting: BI can generate reports that show an organization’s compliance status and any actions taken to address issues. These reports provide specific information about the organization’s compliance efforts.
5. Fraud Detection
Business Intelligence acts like a 24/7 security system for your financial data. It goes beyond spotting unusual transactions—it can actually detect specific fraud patterns like account takeovers or insider trading.
With real-time alerts, compromised accounts can be frozen instantly and shady activity flagged before it becomes a major issue. That means tighter compliance, better security and a stronger reputation that clients can trust.
6. Cash Flow Management
Tired of tracking down where the money went? BI makes it simple by automatically monitoring all company expenses in real time. You’ll know immediately if there’s overspending or a cash shortfall—and even better, you can spot exactly where it’s happening.
It also makes financial planning smoother, helping finance teams allocate budgets and schedule large purchases with confidence.
7. Revenue Management
From forecasting sales to pricing products the right way, BI brings clarity to your revenue strategy. It helps evaluate if projected sales align with your business goals, spot potential risks early, and analyze key factors like competitor pricing, discounts, and product performance.
Even in tough times, BI helps CFOs connect the dots between scattered data to uncover what’s dragging down results—and how to fix it.
Examples of BI Applications in Finance
Many finance companies have implemented business intelligence to improve their operations and decision-making processes. Here are some examples:
1. American Express
In 2020, Americans reported more than 390,000 cases of credit card fraud, which was over 40% higher than the number reported in 2019. This information comes from research published by The Ascent, a service of the Motley Fool. The research also revealed that credit card fraud was the most common type of identity theft experienced by people between the ages of 20 and 39.
As one of the top five credit card companies in the US in terms of active cardholders, American Express has a strong interest in detecting and preventing credit card fraud. However, they must balance these efforts with providing a positive customer experience in order to retain their customers and maintain their business operations.
To enhance the customer experience and reduce the risk of fraud, American Express has developed an advanced fraud detection model using BI tools. Dr. Dmitry Efimov, the VP of Machine Learning Research at American Express, discussed this model, called Gen X, on a recent Emerj AI in Business podcast. Gen X is now in its tenth generation and has continuously evolved since its initial version in 2014. It is the largest model American Express uses to monitor and mitigate fraud within its operations.
2. CitiBank
Citigroup is a major global financial services provider with a presence in over 160 countries and more than 200 million customer accounts. In recent years, the company has shifted to using BI to fuel its growth and improve customer services.
Citibank uses Business Intelligence (BI) to analyze large volumes of customer data, helping them spot opportunities to offer additional products and services. By studying customer transaction data in detail, Citibank gains insights into how their customers manage their finances and what they prefer. This knowledge allows them to customize their offerings, suggesting products and services that match each customer’s specific financial needs. With BI, Citibank can target its marketing more effectively, improving customer satisfaction and making its business more efficient.
Common Challenges in Implementing Financial Business Intelligence
Even with its clear advantages, financial BI can present a few hurdles. Below are some common challenges and tips that will help you stay on track:
1. Data Quality & Consistency
Financial data often lives in different systems and formats, which can create messy or incomplete information.
Pro Tip: Use data integration tools (ETL) to consolidate data into one standardized format, and establish data governance practices to maintain quality over time.
2. Data Security
Sensitive financial data needs strong safeguards to protect it from threats.
Pro Tip: Implement role-based access, encrypt data (both at rest and in transit), and perform regular security audits to stay ahead of vulnerabilities.
3. Resistance to Change
Switching from traditional reporting methods to BI platforms can be a tough sell for some teams.
Pro Tip: Demonstrate success stories, provide training, and choose intuitive BI tools to make the transition smoother and gain buy-in from stakeholders.
4. Cost
BI software, infrastructure, and ongoing maintenance can be pricey.
Pro Tip: Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis, consider more budget-friendly options like cloud-based or open-source solutions, and consider phased rollouts to manage upfront expenses effectively.
Conclusion
Business Intelligence can greatly benefit any Chief Financial Officer by offering an automated system to analyze the company’s past, present, and projected business activities. The financial aspects of a company require consistent attention and oversight. Implementing BI in finance is crucial to proactively managing a company’s financial performance. ScaleupAlly offers Business Intelligence systems tailored for financial services, enabling companies to analyze large amounts of data and generate valuable forecasts. Unlock your business’s full potential, including its products and services, and make informed financial decisions based on the insights provided by BI. Let’s schedule a meeting for today to know more about our BFSI IT solutions and services.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can small businesses benefit from Business Intelligence in finance, or is it primarily for larger corporations?
Absolutely. Small businesses can benefit significantly from Business Intelligence in finance. BI tools are scalable and adaptable, offering insights that can aid in budgeting, forecasting, and strategic decision-making, regardless of the company’s size.
Q: Are there specific industries within finance where Business Intelligence is more prominently used?
Business Intelligence is versatile and applicable across various finance industries. It’s extensively used in banking for compliance and risk management, in investment firms for portfolio analysis, and in e-commerce for dynamic pricing strategies, among other applications.
Q: Can Business Intelligence be integrated with existing financial systems, or does it require a complete infrastructure overhaul?
BI is designed to be adaptable. Most BI tools can be integrated with existing financial systems, minimizing disruption to operations. This facilitates a smooth transition to a data-driven approach without requiring a complete infrastructure overhaul.
Further Reading: Business Intelligence Applications Across Sectors
Related Blogs

Data Warehouse Cost Breakdown: Factors, Pricing Models & Platform Comparison
Discover how much a data warehouse costs in 2025. Explore pricing models, key factors, and platform comparisons to plan your data budget effectively.
Tarsem Singh
Nov 6 ,
14 min read

How Much Do Integrations Cost? [Pricing Breakdown & Key Insights]
Learn how much integrations cost, key factors influencing pricing, hidden expenses to avoid, and effective ways to reduce integration costs.
Tarsem Singh
Nov 6 ,
9 min read

Travel App Development Cost in 2025: A Comprehensive Guide
Travel App Development Cost: The cost to develop a travel app can range anywhere from $10,000 to $100,000 depending on the nature of the app.
Manu Jain
Oct 14 ,
23 min read