Power BI Gateway: A Detailed Overview
Tarsem Singh | January 30, 2025 , 17 min read
Table Of Content
Behind your company’s firewall sits a goldmine of data (sales figures, customer insights, production metrics, etc) all out of Power BI’s reach. It’s a frustration that sparked heated discussions in Microsoft’s development forums back in 2015, as organizations found themselves stuck between the power of cloud analytics and the reality of on-premises data.
Eight years later, the Power BI gateway bridges this divide, but not everyone gets it right.
About 89% of companies still struggle with seamless data integration. That’s where things get interesting.
While most articles paint the Power BI gateway as just another technical requirement, it’s actually transforming how businesses handle sensitive data without compromising security or performance. Some organizations run their gateways for months before realizing they’re barely scratching the surface of its capabilities.
There’s more to this tool than meets the eye.
This blog examines how Power BI Gateway works, steps to install it, and best practices to make the most out of it.
For organizations investing in business intelligence infrastructure, understanding these elements is fundamental to achieving optimal performance and reliability.
Key Takeaways
- Power BI Gateway lets you use cloud analytics without exposing sensitive data.
- Microsoft offers three (3) types of gateways: Personal for solo projects, Standard for small teams, and Enterprise when you need features like clustering and high availability.
- Installation is easy in (7 steps), but put your gateway close to your data sources, and give it enough RAM to handle the workload.
- Most gateway headaches come from simple things: outdated versions, memory bottlenecks, or forgotten password changes. Keep it updated, monitor its health, and you’ll avoid the common pitfalls.
- From banks to factories, organizations are using gateways to turn static data into real-time insights.
What is Power BI Gateway?
- What is Power BI Gateway?
- Why Do You Need Power BI Gateway?
- Types of Power BI Gateway
- How Does Power BI Gateway Work?
- 7 Steps to Install Power BI Gateway
- Troubleshooting Common Issues in Power BI Gateway
- Best Practices for Using Power BI Gateway
- Use Cases of Power BI Gateway in Businesses
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Built by Microsoft to solve the age-old problem of accessing internal data securely, Power BI gateway creates encrypted channels to transport your data and lets you keep sensitive databases tucked safely behind your firewall while still feeding fresh insights to your cloud-based Power BI reports.
The gateway also manages authentication, coordinates refresh schedules, and can even load-balance queries across multiple gateway clusters if you’re dealing with heavy data traffic.
Why Do You Need Power BI Gateway?
Understanding the purpose of Power BI gateway is crucial for unlocking the full potential of your data analysis. Have you ever wondered why some Power BI reports update like clockwork while others sit there, frozen in time? It is how they connect to their data sources. The data gateway in Power BI is the component that enables this connection.
Without a gateway, your stunning Power BI dashboards might as well be fancy screenshots – static and increasingly outdated.
You’ve got valuable data sitting on your local servers, in your SQL databases, or even in those massive Excel files on the finance team’s shared drive. But Power BI in the cloud can’t reach any of that without some help.
In such a case, Power BI gateway becomes essential.
Let me break down the reasons behind the importance of using a Power BI gateway:
- Your databases contain sensitive information. You can’t just expose them to the internet – that’s asking for trouble. The gateway creates a secure tunnel that lets Power BI fetch data.
- Then there’s the refresh factor. Nobody wants to manually update their reports at 6 AM every morning. With a gateway, your sales dashboard can pull fresh numbers automatically while you’re enjoying your morning coffee.
- For companies operating in regions with strict data sovereignty laws, another reason why you need Power BI Gateway is that it ensures compliance by keeping sensitive data local while only sending aggregated results to the cloud.
- Without this gateway, you can create dashboards that pulse with live data, showing sales as they happen or tracking production metrics in real time.
- One more reason to convince you to choose Power BI’s Gateway – companies using automated data refresh through gateways reported saving 200 hours per year.
Types of Power BI Gateway
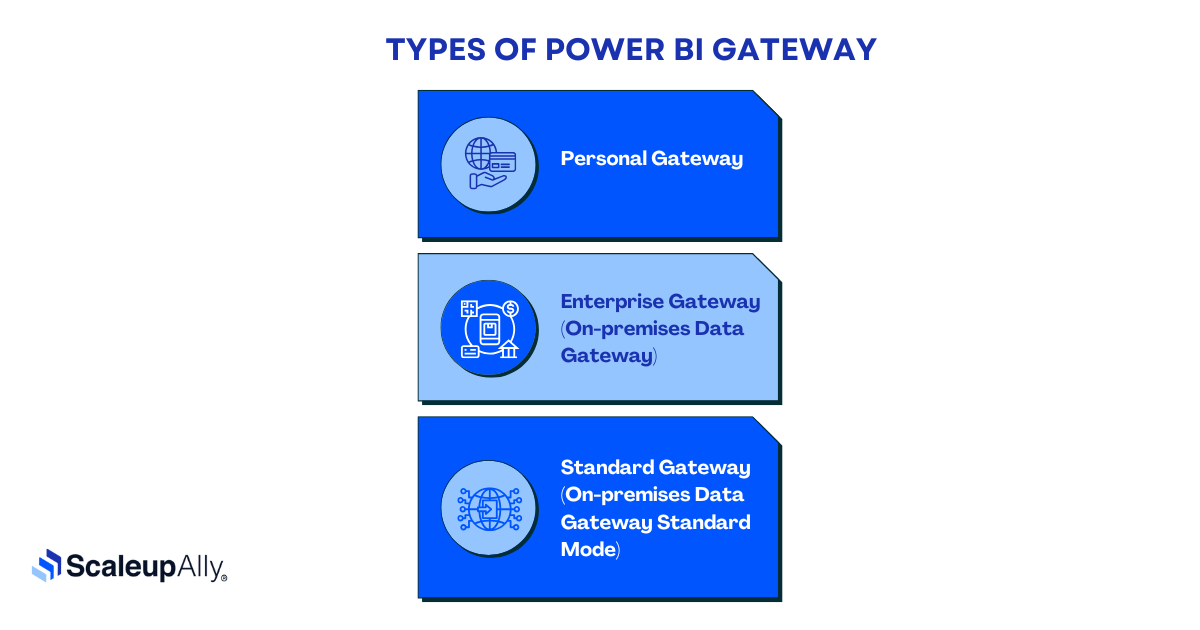
Microsoft offers three distinct Power BI Gateway types, each designed for different scales of operation. Let’s explore which one matches your needs.
1. Personal Gateway
This gateway is great for individual use. It’s designed for individuals who need to refresh their reports without bothering IT.
Key Features:
- Single user access – perfect for individual projects
- Runs under your Windows credentials
- Can’t share connections with teammates
- Limited to Power BI service refreshes only
- Dies when you log off (it stops working when you’re not logged into Windows)
2. Enterprise Gateway (On-premises Data Gateway)
This gateway is reliable, and ready for anything the business throws at it.
Key Features:
- Multiple users can share the same gateway
- Supports live connections to databases
- Handles high-volume data refreshes
- works with other Microsoft services (Analysis Services, Azure Logic Apps)
- Centralized management through admin portal
- Clustering support for high availability
- Advanced monitoring and diagnostics
- Keeps running 24/7 regardless of who’s logged in
3. Standard Gateway (On-premises Data Gateway Standard Mode)
This gateway is not as basic as Personal, and not also as complex as Enterprise, and perfect for small teams that need more than a personal solution but aren’t ready for enterprise-level complexity.
Key Features:
- Supports multiple users like Enterprise
- Works with Power BI, PowerApps, and Flow
- Simpler setup than Enterprise
- Basic load balancing capabilities
- Scheduled refresh support
- No clustering options
- Manageable through Power BI service
Note: Most organizations start with Standard and upgrade to Enterprise when they hit performance bottlenecks or need advanced features.
How Does Power BI Gateway Work?
Has there ever been a case where you sent a secret message using a trusted friend as your messenger? Power BI Gateway works in a similar way – but with enterprise-grade security.
Understanding the Power BI gateway architecture is key to appreciating its efficiency. When you hit refresh on that sales dashboard, your Power BI service in the cloud sends a request to the gateway sitting inside your network. The gateway (your trusted messenger) receives this call and gets to work.
The gateway first checks if you’ve got permission to access that data – no permission, no access. Once you’re cleared, it encrypts a secure tunnel between your on-premises data source and Power BI cloud service. Let’s liken it to a private underground passage that only your data can use.
Instead of the gateway to directly or “blindly” pump data through, it does something different by compressing the information, manages multiple requests simultaneously, and intelligently routes traffic to prevent network congestion.
And this happens through outbound connections only. Your firewall stays tight. The gateway initiates all communication, making your security team happy while keeping your reports updated. And if something goes wrong, the gateway keeps detailed logs of every transaction.
What most people miss is that the gateway can actually queue up requests during high-traffic periods. If too many people are pulling data at once, it’ll prioritize and schedule requests instead of letting your network choke. Smart, right?
7 Steps to Install Power BI Gateway
You need to be alert for this part. Skip a step, and you might find yourself troubleshooting instead of analyzing data. Take your time with these steps, and you’ll save yourself hours of troubleshooting later.
Step 1: Download the Latest Gateway
Head to Microsoft’s download center and get the latest version of Power BI Gateway. Don’t install it on your laptop that goes home with you every night. Pick a server or dedicated machine that stays powered on 24/7. Your future self will thank you.
Step 2: Choose Your Gateway Type
Begin the installer and pick what you prefer – Standard or Personal. We discussed gateway types earlier. This is where that knowledge pays off. Most businesses should opt for Standard unless you’re absolutely sure you need Personal.
Step 3: Sign Into Power BI Service
Use your work account here – the one you use for Power BI service. If you’re getting error messages at this stage, double-check that you’ve got the right permissions in Power BI service.
Step 4: Configure the Gateway
Give your gateway a name that makes sense – like “Sales-Data-Gateway” or “Finance-Gateway”. Skip the creative names – you’ll regret it during troubleshooting. Pick a recovery key too, and store it somewhere safe. Lose this, and you’ll be starting from scratch.
Step 5: Select Network Region
Choose the same region as your Power BI tenant. The gateway will suggest the optimal region, but you can change it if needed.
Step 6: Configure Service Account
The gateway runs as a Windows service. By default, it uses the local service account, but for production environments, consider creating a dedicated service account with just enough permissions.
Step 7: Test Your Connection
Don’t skip this part! Hit the “Test Connection” button in the Power BI service to make sure everything’s working properly. A successful test means you’re ready to start setting up data sources. If it fails? Check your firewall settings – outbound port 443 needs to be open.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Power BI Gateway
Gateway issues can be frustrating and often poorly timed. Let’s tackle the headaches that make data teams pull their hair out.
1. “Gateway Offline”
You’re about to present to executives, and suddenly your gateway drops offline. Classic. Often, this isn’t as dire as it seems. Check if Windows decided to restart for updates, or if your network team changed some firewall rules without telling anyone. A quick fix is to restart the gateway service through Windows Services, and if you are still offline, check the Windows Event Viewer to see what went wrong.
2. Authentication
This one’s common – your gateway’s online but keeps rejecting credentials. Usually happens after password changes or when service accounts expire. Sometimes it’s not even about wrong passwords.
Check if your data source account has its permissions intact. One overzealous admin cleanup, and poof – there go your permissions.
3. Memory
Somtimes, your gateway runs slower than a snail. When that happens, your computer Memory is probably your culprit. The gateway can be a real memory hog when handling multiple concurrent queries.
If you’re seeing performance tank around month-end reports, bump up the RAM allocation in the gateway settings. Keep it under 80% of available system memory, or you’ll just create new problems.
4. Refresh Fails With Cryptic Errors
Nothing is more annoying than a failed refresh with an error message that might as well be in hieroglyphics. Often, it’s about time – either your query is timing out or there’s a time zone mismatch between your gateway and data source.
Set those timeouts higher in the gateway settings, and double-check your regional settings match across systems.
5. The “Ghost in the Machine” Scenario
Sometimes your gateway just acts weird – random connection drops, inconsistent performance, etc. Before you start considering an exorcism, check if you’re running the latest version.
Microsoft regularly patches issues you didn’t even know existed. About 40% of gateway problems resolve with a simple update (based on Microsoft Support Forum analytics).
6. Network Latency Issues
Are reports taking forever to load? Before blaming the gateway, use Performance Monitor to check network latency between your gateway and data sources. If it’s higher than 20ms, you might need to relocate your gateway server closer to your data sources.
Best Practices for Using Power BI Gateway
Your gateway’s running, but is it running at its best of capabilities? After digging through countless implementation stories and hard-learned lessons, here’s what separates the smooth operators from the constant troubleshooters.
1. Location Matters More Than You Think
Don’t stick your gateway on any old server gathering dust in the corner. Keep it close to your data sources – physically and network-wise.
Remember the highway principle: the shorter the distance data travels, the less chance of congestion or delays.
2. Resources Aren’t Optional
That old PC you repurposed as a gateway server is not doing you any favors. Your gateway needs muscle – think 8GB RAM minimum for serious workloads. One major retail chain learned this the hard way during Black Friday when their underpowered gateway crumbled under pressure.
Monitor your gateway’s resource usage for a week. If CPU or memory regularly hits 70%, it’s time for an upgrade before things get ugly.
3. Schedule
Stagger those refresh schedules. Having 20 reports hammer your gateway at 9 AM is like everyone trying to use the office coffee machine right after a meeting.
Spread refreshes throughout the day, and your gateway will thank you with better performance. Also, save heavy-duty refreshes for off-peak hours.
4. Backup Gateway
Have you ever had your car break down with no spare tire? Same panic hits when your only gateway fails. Set up a secondary gateway in cluster mode for anything business-critical. Just like having a backup generator, it may seem excessive until the lights go out.
5. Monitor, Don’t React
Stop waiting for users to tell you something’s wrong. Set up proper monitoring using Power BI Admin Portal and Windows Performance Counters. Watch for patterns – if refreshes start taking longer on Thursdays, figure out why before it becomes a Friday emergency.
6. Keep It Updated, Keep It Running
Updates aren’t just for security. Each new gateway version typically brings performance improvements and bug fixes. But don’t auto-update during business hours. Schedule updates for quiet periods, and always have a rollback plan.
7. Clean House Regularly
Review and clean up gateway configurations quarterly. One financial firm found their gateway was maintaining connections to databases that hadn’t existed for months.
You’ve got to stay ahead of issues before they become problems. Take these practices seriously.
Use Cases of Power BI Gateway in Businesses
Why are companies falling over themselves to set up Power BI Gateway? Let’s find out why:
1. Financial Services & Banking
Power BI Gateway enables banks and financial institutions to maintain compliance while modernizing their analytics. It lets them keep sensitive customer data and transaction records secure on-premises while running real-time analytics for fraud detection, risk assessment, and trading insights.
2. Manufacturing & Production
On factory floors, the gateway connects shop-floor systems and IoT sensors to Power BI dashboards, enabling real-time production monitoring. Teams track equipment performance, predict maintenance needs, and spot quality issues instantly rather than waiting for end-of-shift reports.
3. Healthcare Organizations
In healthcare settings, Power BI Gateway serves as the link between patient records and analytics while maintaining HIPAA compliance. Medical facilities can analyze patient care metrics, resource utilization, and operational efficiency without compromising sensitive health data.
4. Retail & Ecommerce
Retailers use the gateway to unite their point-of-sale systems with inventory management. This enables real-time sales tracking, inventory optimization, and demand forecasting. Store managers can make data-driven decisions about stock levels and merchandising strategies based on current sales patterns.
5. Logistics & Supply Chain
For supply chain operations, the gateway connects warehouse management systems, transportation tracking, and order processing data. This creates end-to-end visibility across the supply chain, helping companies optimize routes, manage inventory levels, and improve delivery times.
6. Educational Institutions
Schools and universities utilize the gateway to connect student information systems, learning management platforms, and administrative databases. This helps track student performance, optimize resource allocation, and identify early intervention opportunities.
7. Government Agencies
Public sector organizations use the gateway to modernize service delivery while maintaining data sovereignty. They can analyze service requests, track resource utilization, and measure program effectiveness while keeping sensitive citizen data secure within government networks.
Conclusion
Just a decade ago, the idea of keeping sensitive data secure while still having real-time cloud analytics seemed like a pipe dream. Now, companies are doing it every day, thanks to this bridge between their protected data and the cloud’s analytical power.
Sure, setting up and maintaining a Power BI gateway takes some work. But consider the alternative: manual data updates, security risks, or worse – making decisions based on outdated information. Whether you’re a small business pulling data from local spreadsheets or a global enterprise connecting multiple data centers, there’s a gateway solution that fits.
Just remember – the gateway you need today might not be the gateway you need tomorrow. As your data needs grow, don’t be afraid to scale up. Start small, monitor carefully, and upgrade when the time is right.
And if you are struggling with Power BI Gateway setup or maybe you’re not sure which gateway type fits your needs, ScaleupAlly’s Power BI specialists have helped dozens of businesses optimize their data connectivity without compromising security.
Book a free 30-minute consultation with our Power BI experts and discover how we can streamline your data integration journey.
We’re here to help turn your data challenges into opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is a Power BI gateway used for?
Power BI Gateway acts as your secure bridge between on-premises data and cloud services. It enables automatic data refreshes, facilitates live queries, and maintains data residency requirements – all while keeping your sensitive information safely behind your firewall.
Q: How many gateways do I need?
The number depends on your data volume and location. Generally, one gateway can handle multiple data sources, but large organizations often deploy several gateways regionally for better performance and redundancy. Consider one gateway per geographical location or major business unit.
Q: Can Power BI Gateway connect to multiple data sources?
Absolutely! A single gateway can connect to various data sources simultaneously – from SQL Server and Oracle databases to Excel files and SharePoint lists. There’s no hard limit on connections, though performance might guide how many you should configure.
Q: Is Power BI Gateway secure for sensitive data?
Yes – security is baked into the core of Power BI Gateway. The gateway encrypts all data in transit using TLS 1.2, enforces role-based access control, and never stores actual data. Plus, it only makes outbound connections, so your firewall stays intact and secure.
Related Blogs

Data Warehouse Cost Breakdown: Factors, Pricing Models & Platform Comparison
Discover how much a data warehouse costs in 2025. Explore pricing models, key factors, and platform comparisons to plan your data budget effectively.
Tarsem Singh
Nov 6 ,
14 min read

How Much Do Integrations Cost? [Pricing Breakdown & Key Insights]
Learn how much integrations cost, key factors influencing pricing, hidden expenses to avoid, and effective ways to reduce integration costs.
Tarsem Singh
Nov 6 ,
9 min read

Power BI for Inventory Management: A Comprehensive Guide
Explore the hidden power of Power BI for inventory management and how it provides businesses with powerful analytics and visualization capabilities.
Tarsem Singh
Oct 8 ,
19 min read