Enterprise Business Intelligence: Key Benefits and Implementation Strategies
Tarsem Singh | April 29, 2025 , 17 min read
Table Of Content
How transformative would it be for your business if you could use enterprise business intelligence (EBI) to prevent adverse events before they happen?
This guide explores how EBI turns raw data into insights that empower companies to stay competitive and make predictive decisions faster that drive success.
Key Takeaways
- Enterprise BI unifies data into a centralized platform, delivering accurate and consistent insights for better decision-making.
- Real-time dashboards, reports, and visualizations provide executives with actionable intelligence to respond quickly.
- Predictive analytics enables forecasting, risk management, and confident strategic planning.
- Automated reporting and streamlined workflows improve efficiency, cut errors, and save time.
- A single source of truth with secure, cloud-based access fosters collaboration, alignment, and seamless anytime insights.
What is Enterprise Business Intelligence?
- What is Enterprise Business Intelligence?
- What Can Enterprise Business Intelligence Do for Your Organization?
- Key Benefits of Enterprise Business Intelligence
- Types of Enterprise Business Intelligence
- What are the Elements of Enterprise Business Intelligence?
- Where Should Enterprise BI Be Integrated?
- Implementation Strategies for Enterprise Business Intelligence
- Cost of implementing Enterprise Business Intelligence
- Future Trends in Enterprise Business Intelligence
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
EBI refers to organizations using tools and technologies to gather data from multiple sources, combine this data, and analyze it to help them make better decisions.
Businesses can then understand the large amounts of data being collected from different departments of the organization to guide their choices.
How Does EBI differ from traditional BI?
Enterprise Business Intelligence is used company-wide, integrating data from various departments to create a unified source of truth. Traditional BI often analyzes smaller data sets within individual departments, providing more localized insights.
What Can Enterprise Business Intelligence Do for Your Organization?
In large organizations, data often gets fragmented across departments or projects, leading to inefficiencies and miscommunication. Enterprise Business Intelligence (BI) solves this challenge by centralizing data and making it more accessible, actionable and strategic.
Here’s how EBI can drive value for your organization:
- Unified Data Collection and Integration
Big enterprises deal with massive volumes of data, often from varied sources. Enterprise BI platforms help consolidate this information into a single, coherent system.
For example, Expedia used enterprise BI to unify its customer data across multiple departments—helping the company successfully meet 10 of its strategic objectives.
- Smarter Data Analysis and Visualization
Modern BI tools let teams query data in plain language, which is then translated into SQL—making it easier for non-technical users to dive deep into analytics and modeling.
Netflix leverages this capability to tailor viewing suggestions based on user behavior, driving over 80% of its content consumption.
- Predictive Analytics for Strategic Forecasting
Using machine learning and advanced modeling, enterprise BI can forecast trends and consumer behavior.
Starbucks, for instance, analyzes data from over 90 million transactions per week to understand purchasing patterns, helping them boost customer engagement and sales.
- Enhanced Decision-Making Support
Enterprise BI helps businesses spot gaps in their offerings and make data-backed decisions.
American Express used predictive analytics to flag up to 25% of Australian customers at risk of account closure—enabling timely intervention through targeted product offerings.
- Real-Time Reporting and Dashboards
Customizable dashboards allow leaders to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) in real time. BI tools offer a full-picture view of operations and customer insights.
Chipotle, with over 2,400 locations, uses BI dashboards to standardize performance metrics and track operational efficiency globally.
Key Benefits of Enterprise Business Intelligence
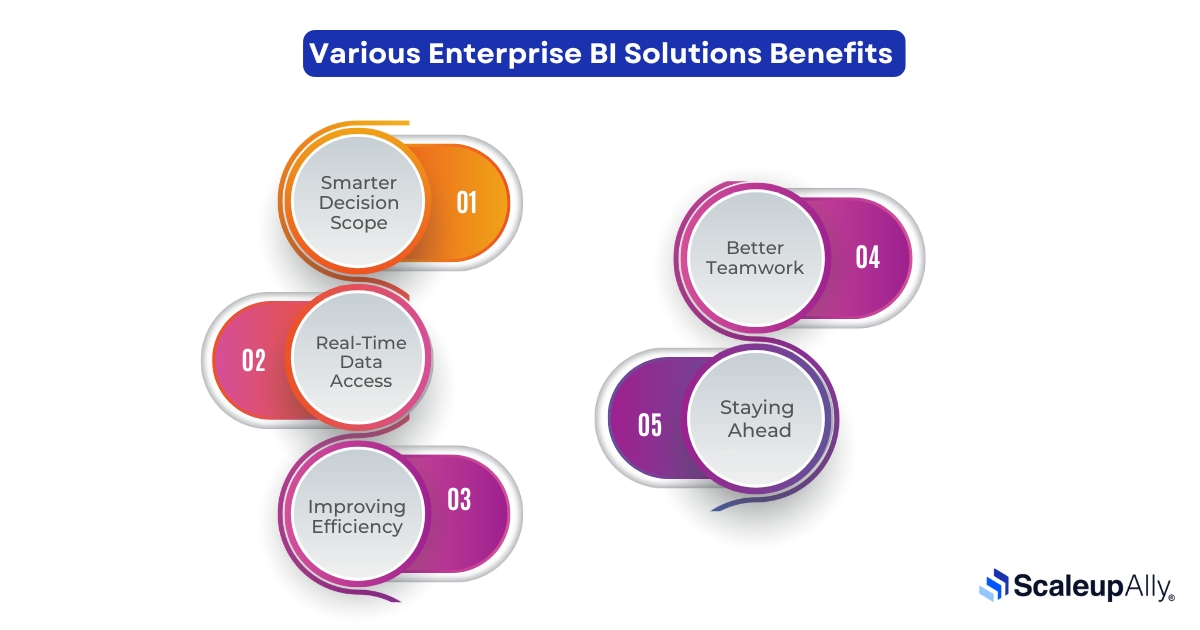
Instead of relying on instincts or assumptions in their regular operations, enterprise grade businesses can use data to guide their decisions and enjoy the following benefits:
1. Smarter Decision Scope
Key decision-makers can now confidently make informed business decisions using detailed reports and visuals of market trends, customer habits, and business operations from Enterprise Business Intelligence reducing uncertainty and improves the quality of decisions by providing organizations with a solid foundation in real data.
2. Real-Time Data Access
Previously, businesses relied on outdated data, leading to poor business decisions. This changed with EBI offering real-time access to data so companies can act timely–a crucial part of every business. Let’s say sales suddenly drop; managers should be able to spot and fix the problem immediately.
This is only possible if managers have access to data to respond faster to customer needs or market shifts. This is what Enterprise Business Intelligence brings to the table.
3. Improving Efficiency
The best way to be highly efficient is by doing things faster, using fewer resources, and in fewer steps. Enterprise business intelligence tools make businesses highly efficient by finding problems and figuring out how to fix them before they become noticed by executives. Enterprise business analytics show companies where processes are slowing down or costing too much for a quick fix.
This data analysis might show delays in the supply chain or inefficiencies in customer service. If these issues are fixed, companies can reduce waste, save time, and improve performance overall.
Plus, EBI tools automate much of the data collection and analysis, saving teams from having to do manual reports.
4. Better Teamwork
EBI combines data from different departments, like sales, marketing, finance, and operations, into one data storage, encouraging team collaboration.
For instance, the marketing team can easily share insights with the sales team to align their goals, or finance can monitor how operational decisions affect revenue. With everyone using the same data, teams can collaborate more effectively and make decisions based on a complete business picture.
5. Staying Ahead
EBI helps businesses stay competitive by identifying trends, opportunities, and potential risks that might not be obvious without deep data analysis.
Businesses can act before competitors by uncovering customer preferences, emerging market opportunities, or shifts in industry dynamics. If a competitor starts losing market share, EBI might help determine why and show how to exploit that weakness.
It also helps with pricing, customer satisfaction, and improving products, which are vital to staying competitive in a fast-moving market.
Types of Enterprise Business Intelligence
Every organization has unique needs, and therefore, different types of enterprise business intelligence approaches are required to serve different purposes.
Here are a few options to help you find the best fit for your business.
1. Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics allows organizations to examine past activities over a certain period. It organizes and displays data using dashboards, reports, and charts. Companies can then get a full picture of their performance and trends or patterns over the historic period.
Descriptive analytics seeks to describe an event, phenomenon, or outcome. This process helps these companies and organizations review their past performance and predict any trends that could come up again in the future, which can be useful when making decisions.
2. Diagnostic Analytics
Diagnostic analytics investigates past occurrences. It examines the “why ” certain trends or events occurred in the past to help find patterns and connections that explain what led to those outcomes.
Companies can detect underlying causes for certain negative outcomes and use that information to make better decisions in the future. It offers a profound understanding of the factors driving events and outcomes integral to business success.
It goes beyond just knowing what happened; it goes further to help you understand why it happened, which can lead to improvements moving forward.
3. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics is an advanced form of data analytics that attempts to answer the question, “What might happen next?” Predictive analytics looks at past data to try and guess what might happen in the future. It uses statistics, machine learning, and algorithms to make these predictions.
Businesses use this type of EBI to predict what might happen next, perhaps understanding customer behaviour, spotting market changes, or identifying potential risks.
When companies have a fair idea of what is likely to occur, they can plan and make decisions to mitigate risks that may come up.
4. Prescriptive Analytics
This enterprise business intelligence strategy goes beyond predicting what might happen; it provides suggestions on what actions you should take to get the best results. It uses advanced models and simulations to guide decision-making instead of simply telling you what the data indicates.
It can determine how many inventory levels a store should have, for example, and how to set prices or adjust your marketing for better results.
It answers the question, “What should we do?” This way, businesses can make more informed choices based on the insights provided.
5. Self-Service BI
Self-service BI allows end business users to analyze data and create visualizations on their own without the help of technical teams. Employees can explore data, create reports, and build dashboards without advanced technical knowledge.
This drives more informed decision-making, resulting in positive business outcomes, increased efficiency, better customer satisfaction, and higher revenue and profits.
6. Operational BI
Another name for Operational BI is real-time business intelligence. It uses the most current data to run a business’s daily operations by providing up-to-the-minute information to help oversee sales, track inventory levels, or manage customer service.
This information is invaluable for making quick decisions and providing companies with the tools to address issues or seize opportunities immediately rather than relying on outdated or delayed data.
What are the Elements of Enterprise Business Intelligence?
When a business wants to succeed in the long run, it needs a strong foundation of information and analysis. These four elements comprise enterprise business intelligence and help companies make thoughtful decisions.
1. Data Cleaning
Data cleaning removes incorrect, corrupted, incorrectly formatted, duplicate, or incomplete data within a dataset. When combining multiple data sources, there are many opportunities for data to be duplicated or mislabeled.
Clean data ensures that the insights derived from it are accurate and reliable when preparing data for analysis. Data cleansing provides fewer errors, making happier clients and less frustrated employees.
2. Reporting & Exploration
This process analyzes data carefully to derive insights by preparing organized reports, charts, and visual tools that show important metrics. These help to summarize the main points that come from studying the data.
At the same time, exploring the data involves going deeper, asking questions, and trying various ways to look at the information.
This allows discovering details that may not be obvious at first and can lead to new chances for improvement or help find problems that may have been missed.
3. Dashboards
Dashboards provide real-time visual summaries of key metrics and data points, often customized for specific organizational roles or functions. They offer a quick overview of the business’s current performance, helping users track goals and make swift adjustments.
Because they’re highly customizable, dashboards are helpful across different industries and verticals. They can include data of all sorts with varying date ranges to help you understand what happened, why it happened, what may happen, and what action you should take.
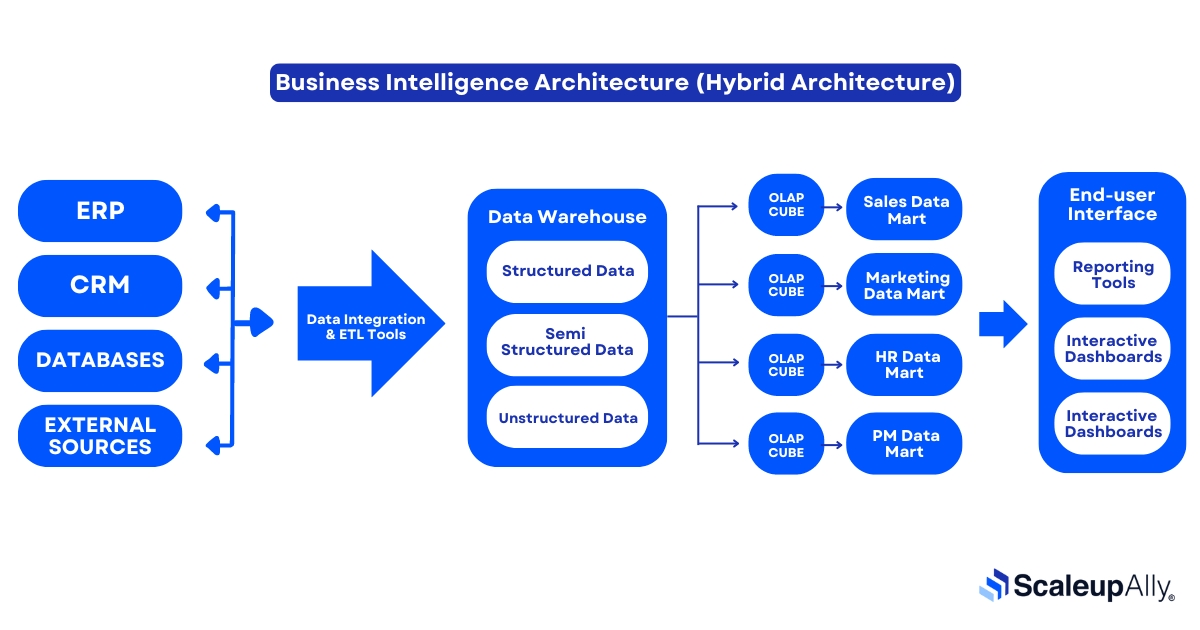
4. Data Storage & Data Integration
Data storage and data integration work together to ensure continuous access to valuable insights. Data storage involves centralized repositories like data warehouses and lakes, where vast amounts of structured and unstructured data are securely stored and organized for easy access.
Data integration combines data from multiple sources, ensuring consistency and accuracy across the organization.
These two elements, when merged, eliminate data silos in businesses and provide a unified view of their data, empowering smarter, more informed decision-making.
Where Should Enterprise BI Be Integrated?
With capabilities like descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics, Enterprise Business Intelligence (EBI) helps organizations pinpoint problem areas, uncover opportunities, and make smarter decisions. To get the most out of EBI, it needs to be integrated strategically across the business.
- Department-Wide Integration
Enterprise BI platforms consolidate data from multiple departments—like sales, finance, and operations—into a unified system. This holistic view helps leaders identify inefficiencies, spot growth areas, and improve decision-making.
Data professionals can then analyze this centralized data to set performance standards and drive accountability across departments. - Cross-Functional Team Integration
Standardizing KPIs across departments ensures alignment between cross-functional teams. EBI makes it possible to create shared dashboards and reports so teams can monitor performance, track objectives, and collaborate on data-driven goals—based on consistent and reliable metrics. - Integration with External Data Sources
Enterprise BI becomes even more powerful when combined with external data. Whether it’s market trends, social media activity, government databases, or supply chain reports, integrating these data streams helps organizations improve forecasting, align budgets, and manage resources more effectively. - Integration with Big Data Technologies
When paired with Big Data, BI transforms into a more advanced analytics powerhouse. This integration allows organizations to extract deeper, more actionable insights from complex datasets. The result? Improved ROI, structured insights, and a clearer direction for long-term strategies.
Implementation Strategies for Enterprise Business Intelligence
1. Conduct a Feasibility Study
Before implementing Enterprise BI, carefully examine what you want from using Business Intelligence and determine what information or data you need to meet those goals. Another important decision you’d need to make is which KPIs to monitor.
In addition, consider the types of reports or dashboards that would be most useful for keeping track. Doing this will ensure the BI system is set up to fit your organization’s needs.
2. Engage Stakeholders and Create a BI Team
Include key stakeholders from different parts of the company, including IT, finance, marketing, and operations, so they are in the loop to provide useful feedback to get the best out of a business intelligence solution.
You must also create a BI team comprising data analysts, IT professionals, and business leaders to guide the project and ensure it runs smoothly. They will ensure the BI solution meets the needs of the entire organization and not just one department.
3. Choosing the Right Type of Enterprise Business Intelligence
Choosing the right approach to business intelligence shouldn’t be rushed. Consider the type of business intelligence that offers ease of use for employees, integration with existing software, and data security.
Cost is also a significant consideration.
It’s important to ensure the BI type fits with your current data systems and can be easily adapted by the entire team. Pick one that suits your organization needs.
4. Establish a Strong Data Governance framework
Have a clear set of rules and guidelines on how data will be handled within your organization.
This means creating policies that keep data accurate, reliable, and safe. Ensure everyone’s trust in the data being used by setting standards for how data should be managed, who can access it, and how it’s protected.
5. Develop a Data Integration Strategy
This involves collecting data from all relevant sources, such as your ERP system, CRM, sales records, and any external sources, and consolidating it in a centralized data warehouse or data lake.
The process typically uses ETL (Extract, Transform, and Load), where data is extracted from its source, cleaned, and organized to ensure it’s in a usable format and then loaded into the central system for further use, such as analysis.
6. Pilot Testing and Iterative Development
Introduce the BI system through a smaller, more manageable project or a limited rollout. This allows you to see how the system works without immediately involving all users or departments. It also allows you to notice any issues early on and gather useful feedback from users.
Their input can help you understand what might need to be changed or improved. By making adjustments along the way, step by step, you’ll increase the chances of the system working efficiently when it’s eventually used on a larger scale.
7. User Training and Change Management
Ensure users know and understand how to use the BI tools properly. To achieve this, organize training sessions and workshops. These can help employees learn and feel more confident using the new system.
It is also helpful to provide continuous support so they can ask questions or get help whenever needed. Besides this, plans should be made to manage any challenges that might come up when introducing the changes.
This way, the company can encourage everyone to use data in their day-to-day work.
Cost of implementing Enterprise Business Intelligence
The cost of setting up Enterprise business intelligence depends on the organization’s size and how sophisticated the BI type would be. A basic EBI system can cost between US$30,000 and US$100,000 for mid-sized organizations.
A larger company requiring a tailored BI solution can spend much more. It is possible to spend anywhere from US$100,000 to over US$1 million. This would cover everything from software and hardware to the services needed to ensure smooth operation.
These figures include software license costs, the time and effort required to integrate the system into existing structures, the staff training to use it, and the regular maintenance needed to keep it running over time.
Future Trends in Enterprise Business Intelligence
Let’s look at how emerging trends are reshaping enterprise business intelligence, driving smarter decisions and greater efficiency.
1. AI-Powered Analytics
Artificial Intelligence is slowly becoming an important part of Business Intelligence. Machine learning and AI-based tools can automate much of the manual work. These tools can analyze large datasets and find patterns that would otherwise be difficult to notice.
Additionally, they can predict future trends based on the data, which allows businesses to make decisions ahead of time. This can also lead to better accuracy.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing allows users to give voice commands or type their questions in everyday language and get answers. By doing this, NLP helps more people access BI tools, even if they aren’t experts in data analysis, which can be useful for many.
It takes away the need for specialized skills and opens up data exploration to a wider audience.
3. Embedded BI
Embedded BI includes analytics and reporting features directly into the tools and software people use daily. Instead of viewing data and reports on another application, users can view important data in the systems they are already familiar with.
This makes it easier and more convenient because it helps users gain insights from data without switching between different programs. As a result, people can make decisions faster and work more efficiently since they can stay focused on their tasks.
Conclusion
Ever feel like you’re running your business in the dark?
Enterprise Business Intelligence can provide the insights needed for your next move regardless of your industry.
Whether you’re making important financial choices, coming up with new marketing strategies, changing your course of action, or even working in a field where decisions could impact lives, having a solid base of business intelligence can be beneficial.
Get equipped with the right tools to discover patterns and make informed decisions, ensuring you’re better prepared for whatever comes next. Contact us today to empower your business and team to make decisions that will drive growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the four concepts of business intelligence?
Data collection, data analysis, data visualization, and decision-making are the four core concepts of business intelligence.
Q: Is Power BI an enterprise tool?
Yes, Power BI is an enterprise-grade BI tool that allows organizations to analyze large-scale data, create interactive dashboards, and generate reports.
Related Blogs

Data Warehouse Cost Breakdown: Factors, Pricing Models & Platform Comparison
Discover how much a data warehouse costs in 2025. Explore pricing models, key factors, and platform comparisons to plan your data budget effectively.
Tarsem Singh
Nov 6 ,
14 min read

How Much Do Integrations Cost? [Pricing Breakdown & Key Insights]
Learn how much integrations cost, key factors influencing pricing, hidden expenses to avoid, and effective ways to reduce integration costs.
Tarsem Singh
Nov 6 ,
9 min read

Power BI for Inventory Management: A Comprehensive Guide
Explore the hidden power of Power BI for inventory management and how it provides businesses with powerful analytics and visualization capabilities.
Tarsem Singh
Oct 8 ,
19 min read