Business Intelligence Strategy: Benefits and Key Components
Tarsem Singh | April 27, 2025 , 15 min read
Table Of Content
A Forrester report showed that about 60 to 73 percent of enterprise data is unused for analytics. Making business decisions while ignoring data is risky, if not careless. Not every decision needs to be intuitive. Sometimes, you need to look at the hard facts.
The difference between industry leaders and followers often comes down to their business intelligence strategy. How are they transforming raw data into insights that drive key decisions in the company?
By the end of this guide, you’ll learn how to implement a business intelligence roadmap, understand both the transformative benefits a proper BI strategy delivers and the essential components required to build one that drives genuine competitive advantage.
Key Takeaways
- A comprehensive BI strategy transforms raw data into actionable insights that drive faster, smarter decisions across an organization.
- To align technology with business goals, start with critical business questions.
- The biggest barriers to success are often organizational: change resistance, skill gaps, and executive misalignment.
- Incremental value delivery keeps stakeholders engaged and funds future development.
- Measure success based on how analytics influence actual results.
What Is a Business Intelligence Strategy?
- What Is a Business Intelligence Strategy?
- What is the Need of a Business Intelligence Strategy?
- Key Components of an Effective BI Strategy
- Benefits of Business Intelligence Strategy
- Steps to Develop a BI Strategy
- Common Challenges in Business Intelligence Strategy Implementation
- Best Practices for Implementing Business Intelligence Strategy
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
A BI strategy is a roadmap that outlines how a business will collect, manage, analyze and transform data into information that can be used for key data-driven decision-making in an organization.
It is a blueprint that shows a company what data should be collected and how to use the collected data for its benefit.
What is the Need of a Business Intelligence Strategy?
We are at a time of data abundance, where businesses are drowning in data, yet thirsty for insights. This paradox explains why companies need a BI strategy.
With a well-thought-out BI strategy, many companies will experience tremendous growth, considering that 21% of digital leaders use data to generate more revenue.
Without a deliberate BI strategy, companies typically experience:
- Data silos where the internally generated data all sit in isolation. This leads to contradictory “truths” and reconciliation meetings because marketing can’t access sales data, operations can’t see customer feedback signals, and finance works with different numbers than anyone else.
- A situation where each department adopts its own analytical tool(s) that hardly integrate with each other, creating massive inefficiencies. The license cost of these tools usually amounts to millions of dollars annually, with nothing to show for it.
- Decision paralysis where executives face conflicting reports from different systems, eroding trust in data altogether. When this happens, companies revert to gut-based decision-making despite their substantial data investments.
A proper BI strategy will provide one thing: confidence. When leaders trust the foundation of their information, they are able to make bolder moves faster when launching a new product or entering new markets.
Key Components of an Effective BI Strategy
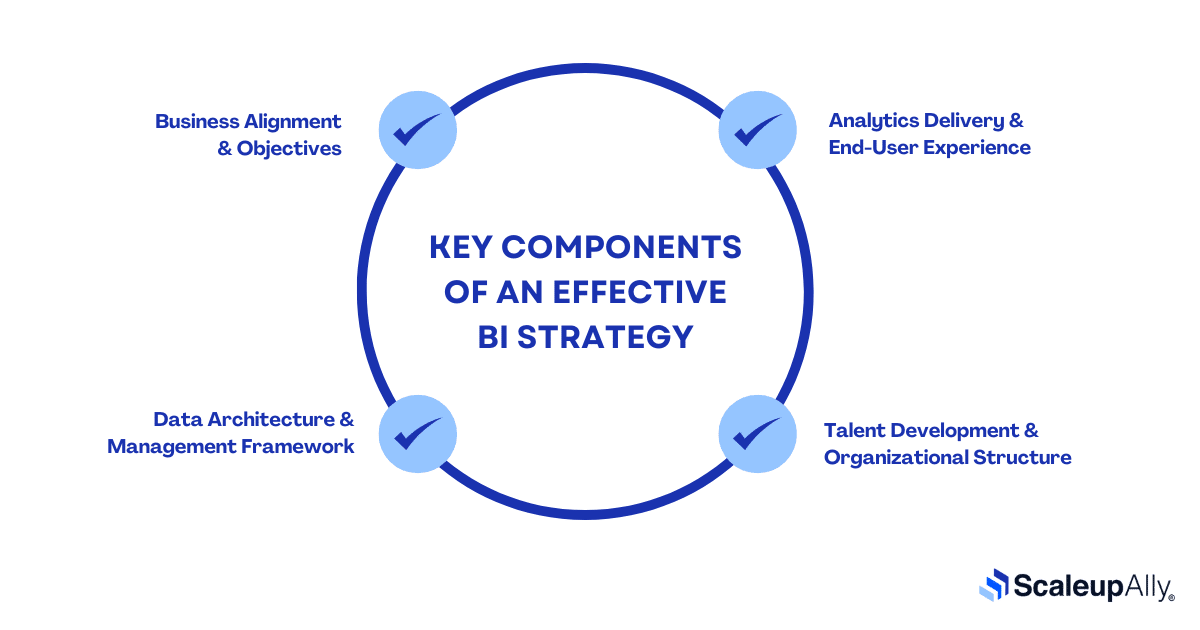
Different elements make an effective BI strategy. These elements do not work in isolation but in unison. The following components, when considered critically, will transform your data from a passive resource into a competitive advantage.
1. Business Alignment & Objectives
The first step in building an effective BI strategy that will support your company’s overall goals is to ask yourself: What would we do differently if we had better information? That single question can help you identify the business decisions that need data support.
From there, map out the key business questions that need answers and connect each one to a specific goal.
For example, if your goal is to increase online sales by 20% in the next 6 months, what you’d want to do is build a dashboard that shows which products are selling the most online. Then analyze customer behavior (e.g., where they drop off in the buying process), and measure the performance of marketing campaigns. This kind of data helps you understand what’s working and what needs improvement, making BI a tool to directly support that goal.
2. Data Architecture & Management Framework
This component is a structure on how data will be collected, stored, moved, and used in your organization. It covers where the data will come from, how it will be integrated, stored, and how it will flow through the company (processes). It also contains governance policies on data quality, security, and accessibility.
Without this foundation, even the most sophisticated analytics tools will produce unreliable results. This leads to bad decisions and loss of trust in your data.
3. Analytics Delivery & End-User Experience
You may generate perfect data, but it becomes worthless if it’s not accessible when and where decisions happen. Your strategy must define how insights will reach stakeholders in formats they can readily use and understand. These could include dashboards embedded in operational systems, mobile reports for field teams, automatic alerts for exceptions, or executive summaries for leadership.
The goal is to get information delivered based on how different roles work. The moment accessing data becomes cumbersome, adoption drops regardless of the quality of insights.
4. Talent Development & Organizational Structure
Even though you will use tools to analyse your data, the success of BI depends on people and not tools. Your BI strategy needs to address how you will develop data literacy across the entire organization. Some teams will need basic skills (like reading dashboards), others will need advanced skills (like analyzing data deeply).
You also need to decide if your analytics teams will be centralized or distributed. Leading organizations create clear career paths for data professionals while also embedding basic data fluency expectations across all business functions.
Benefits of Business Intelligence Strategy
When your BI strategy is implemented thoughtfully, the following benefits will compound over time, giving you an advantage over your competitors.
1. Making Faster, Smarter Decisions Using Real-time Data
In a fast-moving market, speed often trumps perfection. Companies that use BI systems are able to make decisions 3- 5x faster than companies that use traditional reports.
This acceleration is possible because decision makers do not need to wait for weekly or monthly reports. Insights are instantly available when it is needed. The quick access to data enables them to act faster before their competitors do.
2. Improved Everyday Operations
Using BI intelligence improves everyday operations and not only high-level reporting. When data is shared with frontline managers, they can spot:
- anomalies earlier than usual
- Delays or slowdowns, and
- Improvement opportunities
When data is available to frontline managers, companies often save 15–25% in costs within 12–18 months. These savings can pay for the BI systems many times over.
3. Improved Customer Experience
BI systems can be used to improve how customers experience your brand. This happens by combining customer data from all touchpoints (website, support, purchases, etc.). When done correctly, you can spot preferences, patterns in behavior, and past interactions. It matters because it helps you offer personalized experiences that make customers feel understood.
This, in turn, leads to higher customer retention and more customer spending. Instead of reacting to problems, you can anticipate customer needs and act early.
4. Risk Mitigation
Moving beyond customer experience, a sophisticated BI strategy provides early warning systems for market shifts and competitive threats before they escalate into bigger problems. This includes watching for market shifts, competitive threats, and unusual patterns of data.
This is possible by combining external signals (like market trends) with internal data for businesses to see trouble coming long before it’s obvious.
The key takeaway from this is that decisions should be driven by data and not opinions or seniority; everyone at all levels should use facts to guide actions and choices. This creates a shared understanding across the company and encourages collaboration and better decisions.
Steps to Develop a BI Strategy
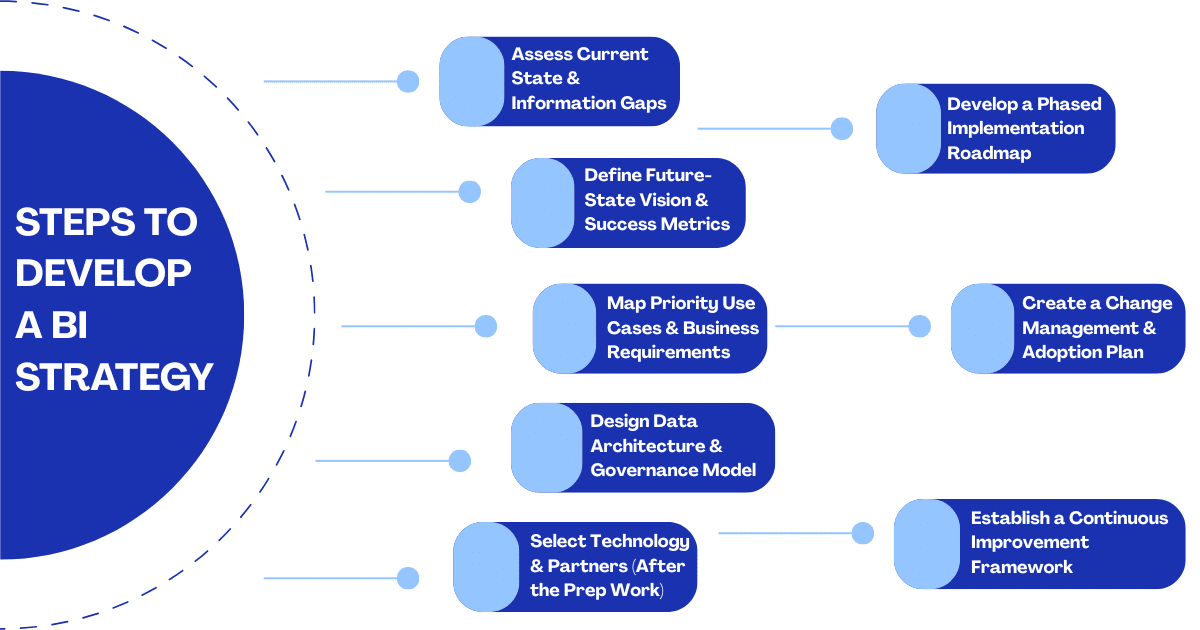
A comprehensive BI strategy takes time and planning. You need to start with goals. However, most companies make the mistake of starting with tools instead. Success comes from aligning BI with business needs and following a clear step-by-step plan, which we’ve outlined below.
1. Assess Current State & Information Gaps
Be honest about where your organization is today and look for gaps where key decisions are made without the right data. Also look for where teams waste time reconciling conflicting reports. Focus on how information flows (or doesn’t) to where decisions happen.
2. Define Future-State Vision & Success Metrics
Know where you are headed. What does actual BI success look like? Tie your vision to real business goals. Avoid vague goals like “be data-driven” but rather focus on clear, specific outcomes like “Reduce time-to-market by 30%” or “Increase customer retention by 15%.” Measure success with implementation milestones (e.g., system launch, training completed) and business results (e.g., faster decisions, improved performance).
3. Map Priority Use Cases & Business Requirements
Focus on what matters most. Not every analytics need is urgent. Pick high-impact areas where better data will lead to better results. For each use case, identify what data is needed, what analysis is required, how insights should be delivered (e.g., dashboard, alert, report), and who will use the information (stakeholders). This helps you stay focused and avoid trying to do everything at once.
4. Design Data Architecture & Governance Model
Once you know your needs, design the system that will support them. This includes data storage (where and how data is kept), data integration (how different data sources connect), and metadata management (tracking and organizing data).
Also, determine how you’ll handle data quality, security, privacy, and regulatory compliance. Define who is responsible for different data areas (both business and IT teams).
5. Select Technology & Partners (After the Prep Work)
Only after completing the previous steps should you evaluate specific technology solutions. Assess potential platforms against your documented requirements, existing environment, and your team’s skills. Decide what to build in-house vs. buy off-the-shelf. When selecting implementation partners, prioritize those with experience in similar business contexts.
The right partners bring both strong technical skills and change management experience to accelerate adoption.
6. Develop a Phased Implementation Roadmap
Break your strategy into manageable projects with clear dependencies and deliverables. Prioritize quick wins that show value early, while building the long-term foundation. The most successful approaches deliver visible business value every 90-120 days while progressively building momentum and trust.
Your roadmap should include clear project phases with timelines, key deliverables and dependencies, skill-building and process updates, and a clear outline of resources needed at each step.
7. Create a Change Management & Adoption Plan
Recognize that technology alone is not enough. People must adopt new ways of working. Develop a structured plan that includes training programs to build skills, internal communications to explain the “why” and “how,” clear success metrics to track adoption, feedback mechanisms to adjust and improve, and incentives to encourage data-driven behaviors to drive user adoption and change decision processes.
Identify champions in each department to lead by example and provide them with extra training and recognition. This step ensures your BI investment translates into actual business impact through consistent and widespread use.
8. Establish a Continuous Improvement Framework
Your BI strategy should evolve and not sit on a shelf. Set up regular check-ins to review what’s working, gather user feedback, and update priorities and tools as business needs change. Also, assign clear ownership for ongoing strategy management, and create a governance committee that:
- Meets quarterly
- Reviews progress and results, and
- Adjusts the roadmap based on outcomes
This will keep your BI efforts relevant and valuable and also ensure your strategy grows with your business.
Common Challenges in Business Intelligence Strategy Implementation
Even with a strong plan, things can go wrong. Knowing the most frequent roadblocks helps you avoid them.
1. Executive Misalignment & Weak Support
When leaders see BI as “just an IT thing,” it’s doomed from the start. Without strong, ongoing executive buy-in, support fades fast, especially during tough moments. To avoid it, tie BI clearly to strategic goals (like growth, efficiency, customer retention) and show early wins that matter to leadership. You should also keep execs engaged by providing outcomes. Don’t be too keen on showing dashboards.
2. Data Quality & Integration Complexities
Many teams underestimate how hard it is to clean and connect data from different systems. Bad data leads to bad insights, which quickly kills trust in the whole system. To avoid it, start small by focusing on one or two high-impact data areas first. Then assign clear data ownership so it’s someone’s job to keep it clean.
3. Not Enough of the Right Skills
You need people who know how to use the insights. Without the right skills, even great tools sit unused. The best way around this is to help business users understand data and how to act on it. Building hybrid roles that connect tech experts with decision-makers while encouraging analytical thinking across all departments, not just IT, also helps.
Best Practices for Implementing Business Intelligence Strategy
Even the best plans can fail during execution. The difference between success and failure often comes down to how well you implement. Here are some best practices for implementing a business intelligence strategy.
1. Start With Business Questions, Not Available Data
Focus on key decisions that drive your business, then figure out what data helps make those decisions better. For example, if you are a consumer goods company, shift your focus from gathering all data to answering three key questions: which products to develop, which promotions to run, and which stores to prioritize for distribution. This focus will deliver tangible value within months rather than years.
2. Adopt Iterative Implementation With Clear Value Milestones
Avoid huge, one-time launches. Instead, break the BI strategy into manageable phases. For example, if you are a healthcare system, deliver quarterly updates, each focusing on specific clinical or financial outcomes.
It works this way because early wins fund later phases, and stakeholders see results quickly, which builds momentum. Each milestone also delivers value on its own, without relying on future phases.
3. Cultivate Cross-Functional Data Ownership
Data ownership isn’t just for IT. Business stakeholders must ensure that data drives decisions. A manufacturing company should create “data product managers” who bridge business and technical roles, and take end-to-end responsibility for key data domains like customer info or production metrics. These cross-functional roles will ensure that technical tools translate into real business value.
Conclusion
BI isn’t just about tech; it’s about changing how decisions are made at all levels of the organization. To succeed, focus on balancing technical tools with adoption. Without it, your sophisticated systems won’t create value.
To recap, understand your current data and decision-making gaps. Then prioritize decisions that will benefit most from better data, rather than trying to solve everything at once.
If you are ready to start transforming your organization’s approach to data, contact our analytics strategy team. We’ve helped organizations across industries develop and implement BI strategies that deliver measurable business impact within months.
The data you need already exists. The question is, will you be the one to unlock its value?
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the main goal of a BI strategy?
The primary goal of a BI strategy is to transform raw data into actionable insights that improve business decisions across all levels of an organization. It aims to create a sustainable competitive advantage by making better, faster decisions based on evidence rather than intuition alone.
Q: How do you align a BI strategy with business goals?
Start by identifying key business objectives and the decisions that drive them. Map each analytics initiative to specific business outcomes with measurable metrics. Involve business leaders in defining requirements and prioritizing use cases. Regularly review alignment as business priorities evolve.
Q: Which tools are commonly used in BI strategies?
Common tools include data warehousing platforms (Snowflake, BigQuery), ETL/ELT solutions (Fivetran, dbt), visualization tools (Tableau, Power BI, Looker), and analytics platforms (Alteryx, SAS). The best tool depends on your specific use cases, existing technology stack and team capabilities.
Q: What are the biggest mistakes in BI implementation?
The biggest mistakes include starting with technology rather than business requirements, underestimating data quality challenges, neglecting change management, attempting too many things at once, failing to measure business impact and treating BI as an IT project rather than a business transformation initiative.
Related Blogs

Data Warehouse Cost Breakdown: Factors, Pricing Models & Platform Comparison
Discover how much a data warehouse costs in 2025. Explore pricing models, key factors, and platform comparisons to plan your data budget effectively.
Tarsem Singh
Nov 6 ,
14 min read

How Much Do Integrations Cost? [Pricing Breakdown & Key Insights]
Learn how much integrations cost, key factors influencing pricing, hidden expenses to avoid, and effective ways to reduce integration costs.
Tarsem Singh
Nov 6 ,
9 min read

Power BI for Inventory Management: A Comprehensive Guide
Explore the hidden power of Power BI for inventory management and how it provides businesses with powerful analytics and visualization capabilities.
Tarsem Singh
Oct 8 ,
19 min read